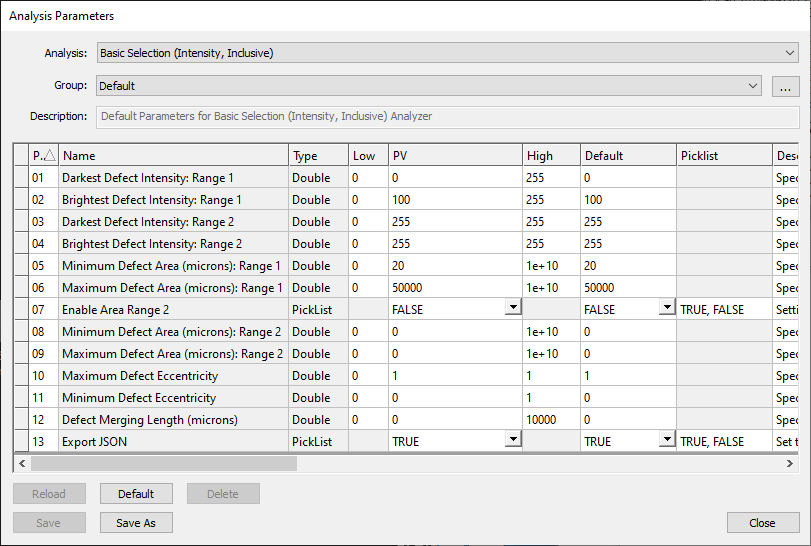
Basic Selection Analyzer
Basic selection is an nSpec analysis that uses computer vision to detect anomalies on non-patterned, bare samples. There are three variants of basic selection: Basic Selection (Contrast, Morphological Range), Basic Selection (Intensity, Exclusive), and Basic Selection (Intensity, Inclusive). Each uses different methods for detecting defects.
Basic Selection (Contrast, Morphological Range)
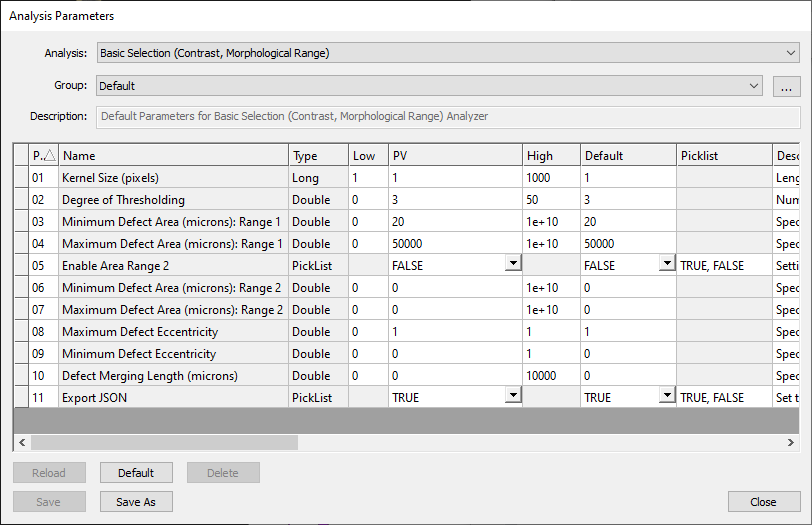
Basic Selection (Contrast, Morphological Range) uses contrast-based computer vision methods to detect defects. It applies the morphological gradient operation to the image to determine where potential defect edges are present.
The Kernel Size (pixels) parameter determines the size of the kernel used to perform the morphological gradient operation. The larger the expected defect size, the large the kernel should be. Using a smaller kernel size will increase computational resources needed for the analysis. The Degree of Thresholding sets the value for the number of standard deviations a pixel must be from the mean to be considered defective, with a larger degree being more selective.
Basic Selection (Intensity, Exclusive)
For the Basic Selection (Intensity, Exclusive) analysis, users define the pixel intensity of what should be considered the background using the Darkest Background Intensity and Brightest Background Intensity parameter values. The background by definition does not contain defects. Pixel intensities outside of the background range are potential candidates for defects. Users can then filter the potential candidates by size, using the Minimum Defect Area and Maximum Defect Area parameters. Users can set up to two ranges for defect size, and can also set a range for defect eccentricity.
In the screenshot below, pixels with intensity 70-200 are considered to be part of the image background. Therefore, pixels with intensity 0-70 and 200-255 can be potential defects. Within these intensity ranges, artifacts of size 20 - 50,000 μm2 are considered to be defects.
Basic Selection (Intensity, Inclusive)
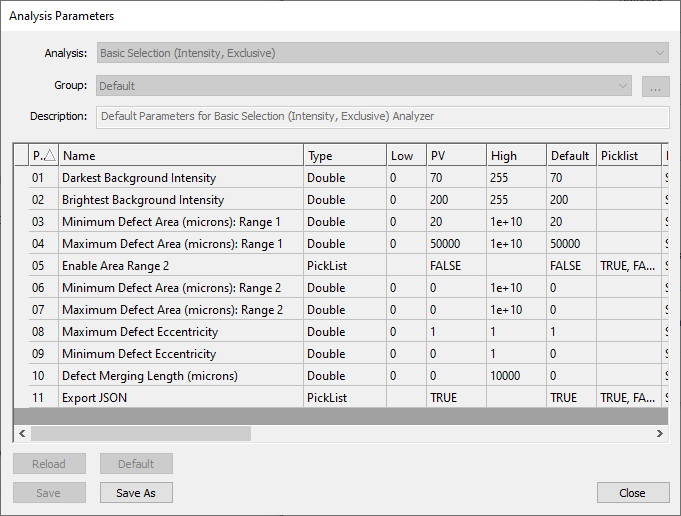
For the Basic Selection (Intensity, Inclusive) analysis, instead of defining the background like in the previous analysis, users define the pixel intensity for defects using the Darkest Defect Intensity and Brightest Defect Intensity parameter values. Users can similarly filter potential defect candidates by size, using the Minimum Defect Area and Maximum Defect Area parameters.
In the screenshot below, pixels with intensity 70-200 are considered to be the background. Therefore, pixels with intensity 0-70 and 200-255 can be potential defects. Artifacts of size 20 - 50,000 μm2 are considered to be defects.