nSpec v0.22.1.4 External Release Notes
nSpec Version 0.22.1.4
Release Date:
Documentation Updated:
Major Features: Fix to Custom Reporter, Cropped Image Analysis in Database
Overview
This patch release includes bug fixes for the Custom Reporter, Cropped Image Analysis export, and an issue affecting job groups with job properties set.
This version also contains several minor updates including tilt correction in the exported Flatness Report and improved text readability in the Surface Scattering Report. Additionally, the Cropped Image Analysis defect data will now be added to the database, enabling this data to be utilized with Custom Reporter and Custom Exporter.
Upgrading to v0.22.1.4
Library Update Not Required
If upgrading from a version more than 1 release prior, please reference all intermediate release notes for upgrade steps for each version.
New Features
Highlights
NSPEC-5916: Tilt removed from Flatness Report PNG
When viewing the exported Flatness Report PNG file, the report will now display data that has been corrected for any tilt present in the stage, as determined by Predictive Autofocus.
However, when viewing the Flatness Report within nView, the rendering will continue to show the original raw data, which includes tilt. This enables users to perform troubleshooting tasks using the Flatness Report in nView, for example, visualizing any tilt present.
The accompanying exported focus point CSV file will continue to contain the original raw focus point data.
See Appendices section for more on flatness reports.
NSPEC-6908: Add the Cropped Image Analysis data into the database.
After running the Cropped Image Analysis, the resulting data will be added to the database. This allows for the cropped image defect data to be used with tools like Custom Reporter and Custom Exporter.
New Features Changelog
Bug Fixes
Highlights
NSPEC-6469: If first job in a job group for multiple wafers is set with job properties, first job ignored
This release fixes a bug in which the first job in a job group will be ignored if A) the autoloader is used, B) the job group is being performed on multiple wafers, C) the first job is set with job properties.
For example, if running a job group on multiple wafers and the first job is set with the job property to export a flatness report, the flatness report will not be exported but all other subsequent jobs will be performed.
Changelog
Appendices
Flatness Report
Overview
The Flatness Report is an addition to nView that renders the surface of any nSpec scan. This can help you understand the surface topology of your samples. This feature can also help you troubleshoot autofocus settings by allowing you to visualize your sample surface when a Surface Prediction algorithm is not characterizing surface topology optimally. This is especially true if you use this in tandem with the new feature to save autofocus images during the scan.
The Flatness Report is available for all scans that included an autofocus step that generated a Predictive Focus map.
Note: previous versions of this documentation equated “flatness” to “bow”, which is inaccurate. Flatness and bow measurements are not equivalent terms. For more information about the differences between the terms, we recommend reading the definitions in http://www.mast-tech.com.tw/semi-definition.pdf.
Scanning
The Flatness Report will be available for any scan that used a surface prediction algorithm.
Reporting
Accessing the Report within nView
In addition to the Flatness Report now available to all scans, nSpec now also supports a special scanning mode that will allow you to perform a Flatness Analysis without vacuum so that a measurement can be performed without the stage vacuum pulling the sample flat during the measurement.
To utilize, simply check the new No Vac option checkbox on the Jobs dialog:

To find the Flatness Report for a scanned wafer, all you need to do is navigate to the new Flatness Report option (ctrl+6) when viewing results in nView:
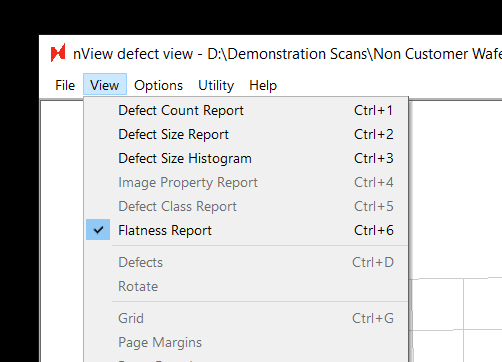
On the left the report shows an interactive 3-dimensional rendering of the sample. On the right, the same data is rendered from a top-down perspective. The scale bar in the center displays the nSpec stage Z coordinates corresponding to a given color on the two maps.
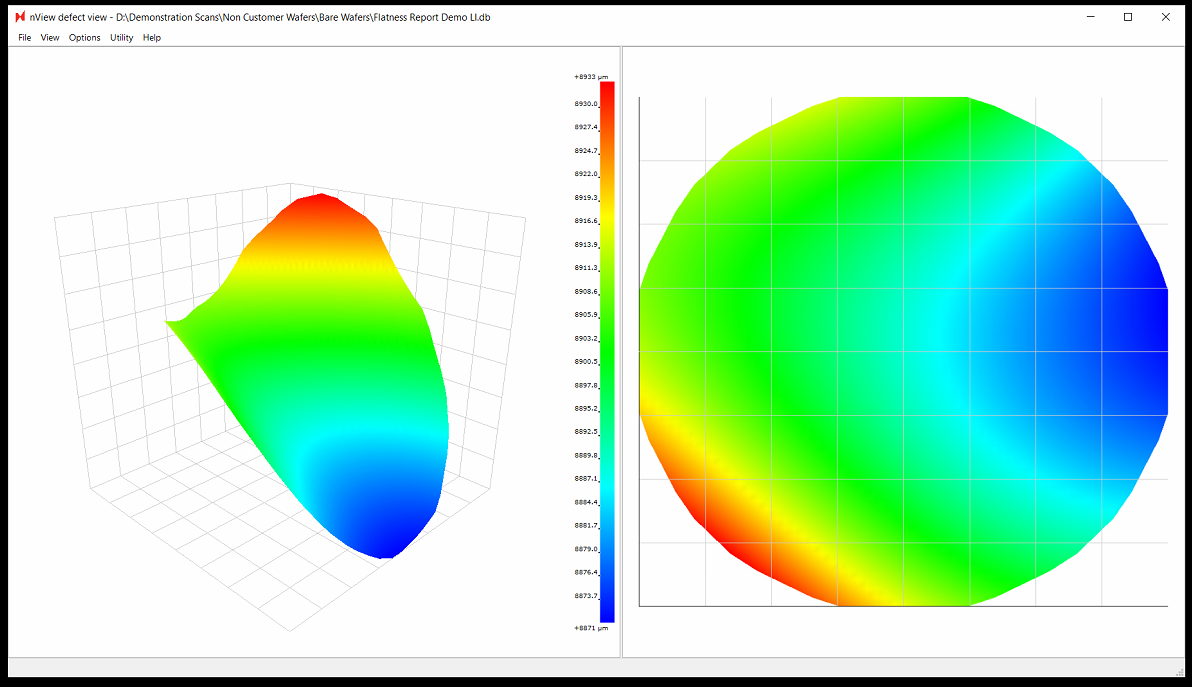
Note: when viewing results in nView, the Flatness Report values includes any potential tilt in the stage. However, the values in the exported Flatness Report PNG file are corrected for tilt.
Exporting a PNG Report
Since the Flatness Report doesn’t require an explicit analysis to be performed and is extended to all scans, triggering a Flatness Report is a bit different from other exports in nSpec. Elsewhere you have analysis parameters to control JSON, CSV, and image exports.
To export a full flatness report, you need to use a new Job Property:
Name | Value Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ExportFlatnessReport | Bool (TRUE, FALSE) | Enable flatness report export after scan succeeds |
After the scan is completed, a folder will be added in the location dictated by the ReportExport program option.
This folder will be named FlatnessReport_<Scan_ID> (ex. FlatnessReport_001).
Within this folder will be two files:
<Sample ID>_<Scan_ID>_Flatness_Report.png
<Sample_ID>_<Scan_ID>_Focus_Points.csv
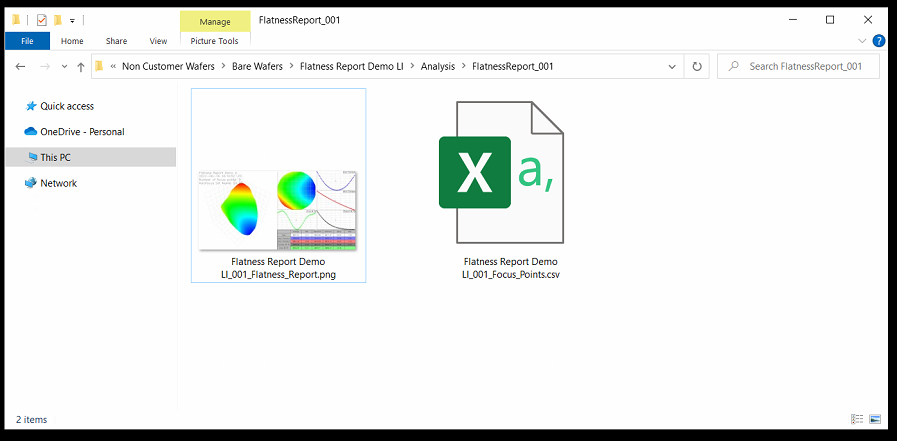
Since our stages have their Y axis flipped (0,0 is the TOP left of the stage when facing the nSpec machine) the values will appear flipped:
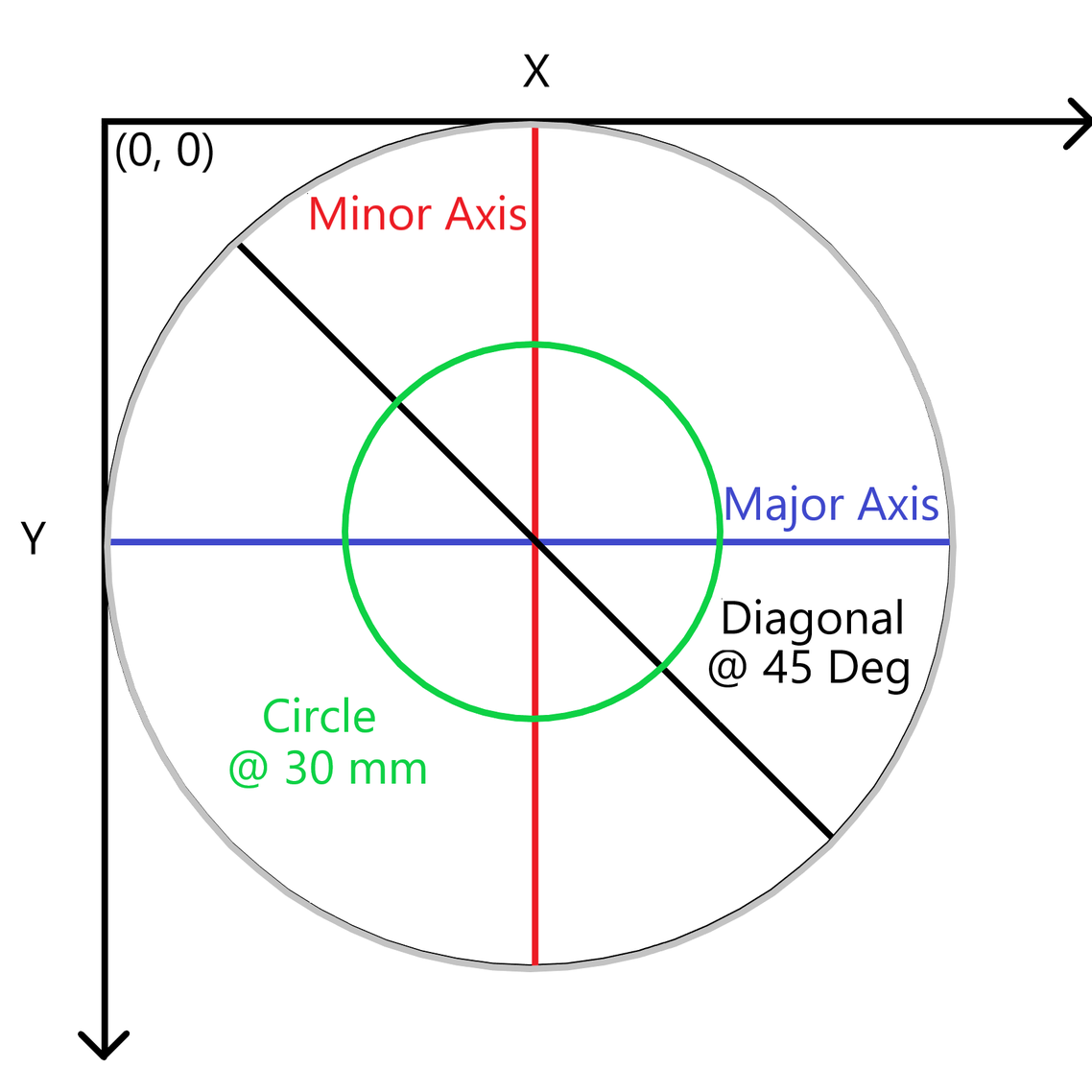
The image export has the following information, corrected for any potential tilt in the stage:
3D orthogonal view (scatter plot)
Top-down view
Major axis slice
Minor axis slice
45 degree slice
30 mm ring slice (hardcoded 30 mm)
Table of calculations: Average value, Standard deviation, Min, Max, Bow, Warp
An example Flatness Report PNG:
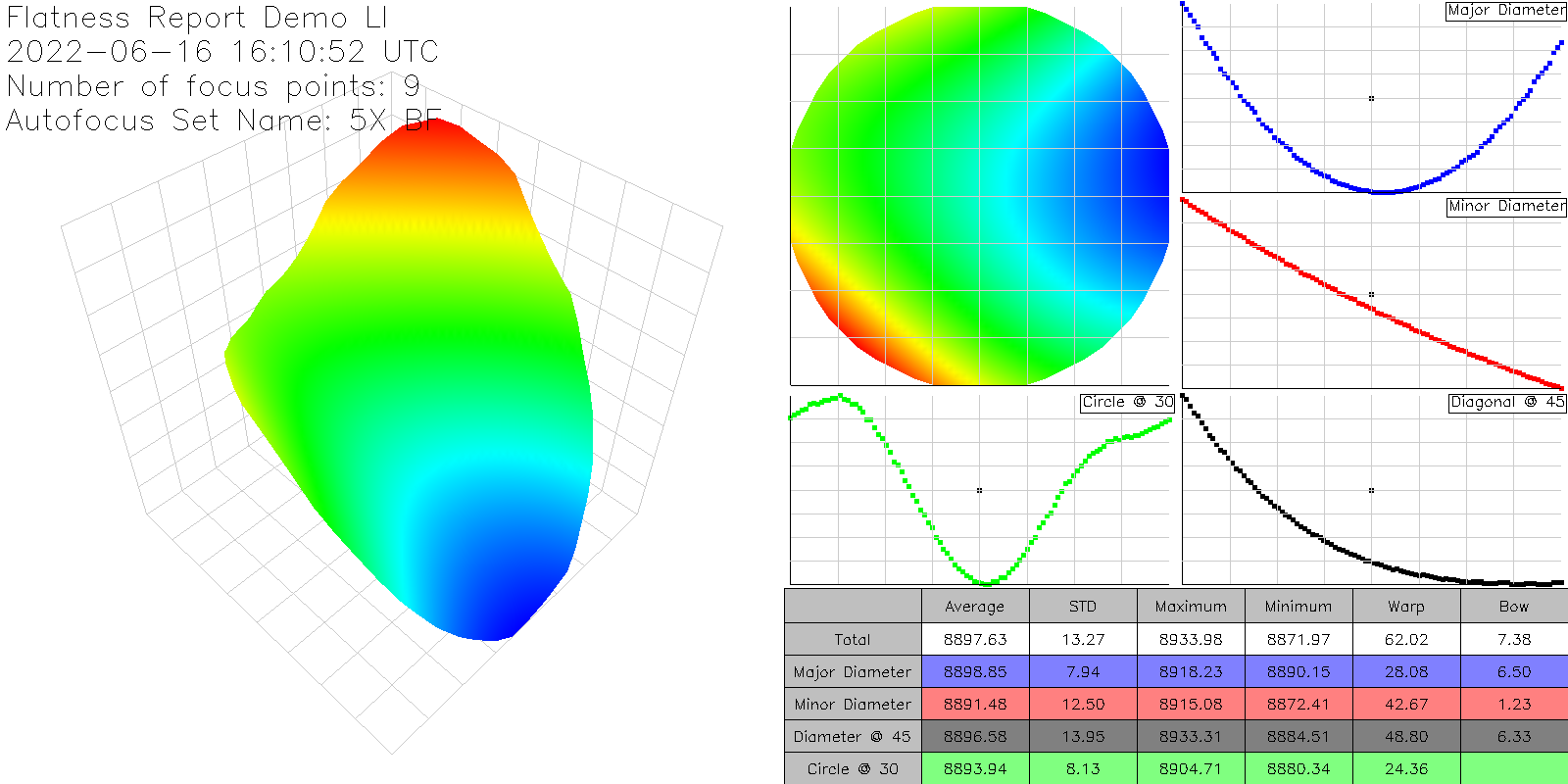
As well as a raw and simple CSV export of the focus points collected during the scan:
X (µm) | Y (µm) | Z (µm) |
|---|---|---|
103349.9 | 133045 | 8900.789 |
61099.9 | 133045 | 8913.055 |
61099.9 | 90795.02 | 8907 |
61099.9 | 48545.02 | 8933.602 |
103349.9 | 48545.02 | 8905.148 |
103349.9 | 90795.02 | 8890.289 |
145599.9 | 90795.02 | 8876.977 |
145599.9 | 48545.02 | 8891.602 |
145599.9 | 133045 | 8884.781 |
